In laboratory settings, pH indicators are essential for determining solutions’ acidity or alkalinity. Among the various indicators available, thymolphthalein stands out due to its distinctive color change in highly alkaline conditions. Unlike common indicators like phenolphthalein, which changes color in a lower pH range, thymolphthalein is specifically suited for measuring strong bases.
This blog explores what makes thymolphthalein a unique pH indicator, its chemical properties, its working mechanism, and its applications in different fields.
What is Thymolphthalein?
Thymolphthalein is an organic compound used as a pH indicator in laboratory experiments. It belongs to the phthalein family, which includes widely used indicators such as phenolphthalein.
Chemical Properties of Thymolphthalein
- Chemical Formula: C28H30O4
- Molecular Weight: 430.54 g/mol
- Appearance: White to pale yellow crystalline powder
- Solubility: Soluble in alcohol, slightly soluble in water
- pH Range: 9.3 – 10.5
- Color Change:
- Colorless in acidic and neutral solutions
- Blue in alkaline solutions (pH > 9.3)
Thymolphthalein’s distinct color shift at high pH levels makes it ideal for detecting strong bases in analytical chemistry.
How Does Thymolphthalein Work as a pH Indicator?
Thymolphthalein functions as a pH-sensitive dye that responds to changes in hydrogen ion (H⁺) concentration.
Mechanism of Color Change
- At pH < 9.3, thymolphthalein exists in its protonated (non-ionized) form, appearing colorless.
- As the pH increases above 9.3, it loses protons (deprotonation) and transforms into its ionized (alkaline) form, which is blue.
- The intensity of the blue color increases with higher pH levels, peaking around pH 10.5.
This color change is reversible, meaning that lowering the pH below 9.3 will make the solution colorless again.
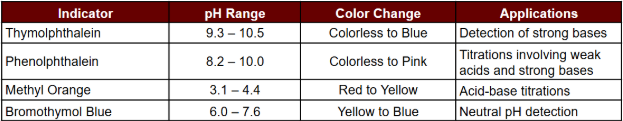
Comparison with Other pH Indicators
Applications of Thymolphthalein in Laboratories
Thymolphthalein is widely used in analytical chemistry, chemical manufacturing, and biological research due to its specificity for high-pH environments.
1. Acid-Base Titrations
In titration experiments, thymolphthalein is used to determine the endpoint of reactions involving strong bases like sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- It remains colorless until the pH reaches 9.3, where it starts turning blue.
- The appearance of blue color signifies the completion of the reaction.
- This makes it valuable in quality control tests in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
2. Testing Alkalinity in Industrial Processes
Many industrial applications require precise pH measurements, especially in:
- Water treatment plants to test alkalinity levels.
- Chemical manufacturing for monitoring pH in production lines.
- Soap and detergent production where strong bases are involved.
Using thymolphthalein as an indicator ensures that the process remains within the desired alkaline range.
3. Urinary and Medical pH Testing
The pH of bodily fluids, such as urine, can provide insight into metabolic and kidney functions. Thymolphthalein is sometimes used in medical diagnostics to:
- Detect alkaline urine, which may indicate infections or metabolic imbalances.
- Assist in diagnosing kidney disorders by monitoring pH fluctuations.
While litmus paper and universal indicators are commonly used for routine tests, thymolphthalein is preferred when focusing on highly alkaline urine samples.
4. Invisible Ink and Forensic Applications
One of the more unconventional uses of thymolphthalein is in invisible ink.
- Thymolphthalein solutions are colorless when applied to paper.
- When exposed to an alkaline solution (e.g., ammonia vapor), the ink turns blue, revealing hidden text.
- This property makes it useful for security markings, forensic science, and educational experiments.
5. Biological and Chemical Research
Thymolphthalein is used as a pH marker in biochemical studies involving enzyme reactions and cell culture media.
- Certain enzymes function only within specific alkaline pH ranges.
- Researchers use thymolphthalein to ensure that solutions remain within the required pH window for accurate results.
This makes it an essential tool in biotechnology and pharmaceutical research.
Advantages of Using Thymolphthalein
Thymolphthalein offers several benefits over other pH indicators, particularly in high-pH applications.
1. Specificity for Strong Bases
Unlike phenolphthalein, which begins to change color at a lower pH, thymolphthalein is more suited for highly alkaline conditions.
2. High Sensitivity
Its sharp color transition ensures precise detection of alkaline endpoints in titration and industrial processes.
3. Reversible Color Change
The reversible nature of thymolphthalein makes it useful in dynamic pH monitoring applications.
4. Versatility
From scientific research to forensic applications, thymolphthalein has multiple uses beyond traditional acid-base reactions.
Conclusion
Thymolphthalein is a highly effective pH indicator with applications in chemical analysis, industrial quality control, medical diagnostics, and forensic science. Its unique ability to detect strong bases sets it apart from other pH indicators like phenolphthalein.
Whether used for titration experiments, pH monitoring, or hidden ink applications, thymolphthalein remains a valuable tool in scientific and industrial сайт.